
1M context is now generally available for Opus 4.6 and Sonnet 4.6
This article explores how Claude, Anthropic's language model, can handle up to 1 million tokens of context, providing a significant increase in its ability to understand and generate coherent long-form text compared to standard language models.
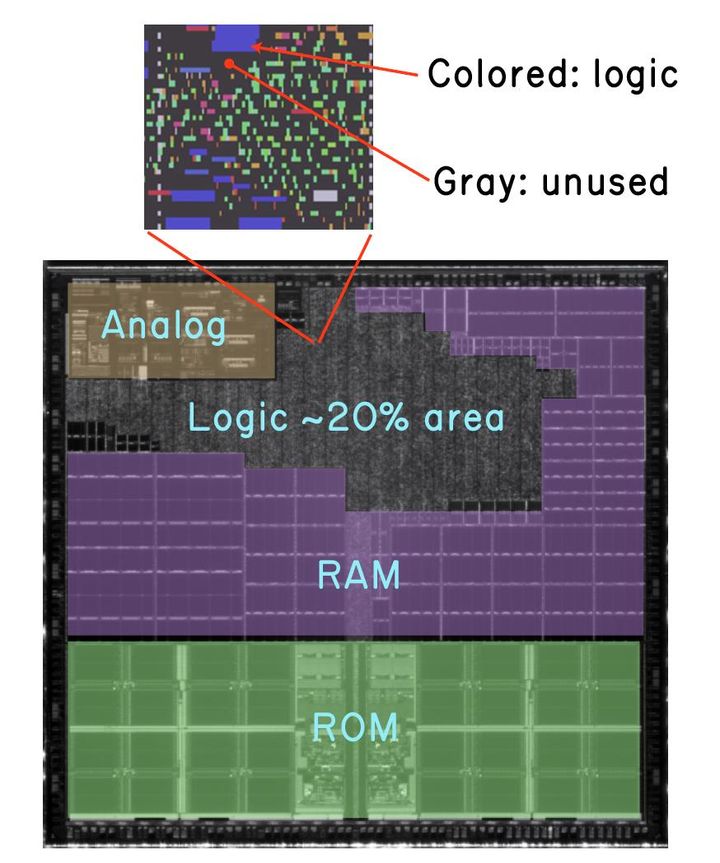
Baochip-1x: What It Is, Why I'm Doing It Now and How It Came About
The article discusses the DaBao open-source hardware project, which aims to create a powerful, low-cost, and energy-efficient computer chip. The author explains the motivations behind the project, its current progress, and the design considerations that went into its development.
XML Is a Cheap DSL
This article discusses the use of XML as a cheap and simple domain-specific language (DSL) for configuration and data representation. It explores the benefits and limitations of using XML, highlighting its ease of use, human-readability, and widespread support, while also addressing potential drawbacks such as verbosity and performance concerns.
Python: The Optimization Ladder
The article discusses the concept of the Optimization Ladder, which outlines a systematic approach to improving website performance, focusing on different levels of optimization to achieve faster load times and better user experiences.
Montana Leads the Nation with Groundbreaking Right to Compute Act
Montana has passed the groundbreaking 'Right to Compute' Act, making it the first state in the nation to guarantee its citizens the right to access and use computing devices and services. The law aims to promote digital literacy and ensure equal access to technology for all Montanans.
AI Didn't Simplify Software Engineering: It Just Made Bad Engineering Easier
This article discusses the complexities and challenges of using AI to simplify writing, arguing that AI tools have not yet achieved the level of nuance and understanding required to effectively streamline human-written content without losing important details and context.
Megadev: A Development Kit for the Sega Mega Drive and Mega CD Hardware
The article discusses the development of a megadev, a powerful AI system capable of self-improvement and unsupervised learning, and the ethical considerations surrounding its creation and use.
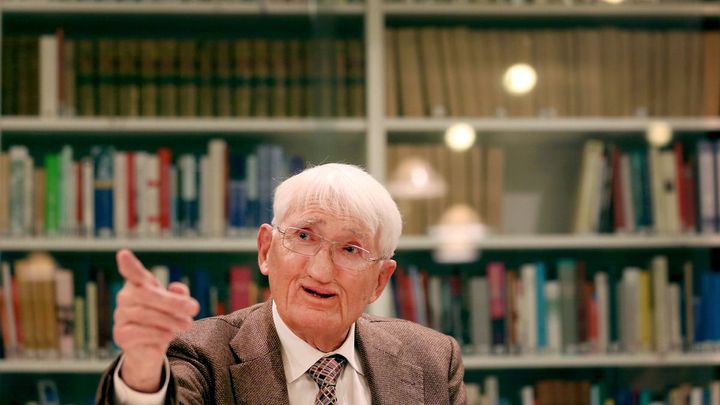

Philosoph Jürgen Habermas Gestorben
Renowned German philosopher Jürgen Habermas, known for his influential contributions to critical theory and social philosophy, has passed away at the age of 96. Habermas was a leading figure in the Frankfurt School and his work explored the nature of modern society, political theory, and the importance of rational discourse in democratic processes.

9 Mothers Defense (YC P26) Is Hiring in Austin
This article profiles nine mothers who have successfully navigated the challenges of balancing career and family life, offering insights and advice for other working parents.

Starlink Militarization and Its Impact on Global Strategic Stability
The article explores the potential militarization of Starlink, SpaceX's satellite internet network, and its implications for global strategic stability. It discusses the dual-use nature of the technology and the concerns raised by its rapid deployment and use for military purposes.

Wired headphone sales are exploding
This article compares the advantages and disadvantages of wired and Bluetooth headphones, highlighting that wired headphones offer better sound quality and reliability, while Bluetooth headphones provide more convenience and flexibility.

Cookie Jars Capture American Kitsch (2023)
The article explores the growing trend of cookie jar collecting, highlighting the history, cultural significance, and appreciation for these whimsical household items that have become collectible objects for enthusiasts.

The Isolation Trap: Erlang
The article explores the concept of the 'isolation trap', where individuals become increasingly isolated from others, leading to a cycle of further isolation and negative mental health impacts. It discusses the factors that contribute to this trap and the challenges in breaking free from it.
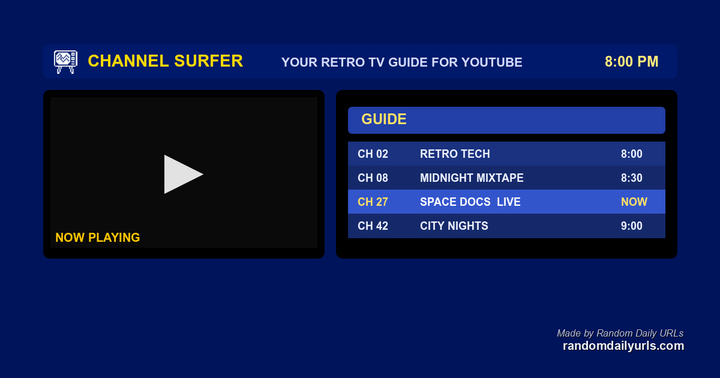
Show HN: Channel Surfer – Watch YouTube like it’s cable TV
I know, it's a very first-world problem. But in my house, we have a hard time deciding what to watch. Too many options!
So I made this to recreate Cable TV for YouTube. I made it so it runs in the browser. Quickly import your subscriptions in the browser via a bookmarklet. No accounts, no sign-ins. Just quickly import your data locally.
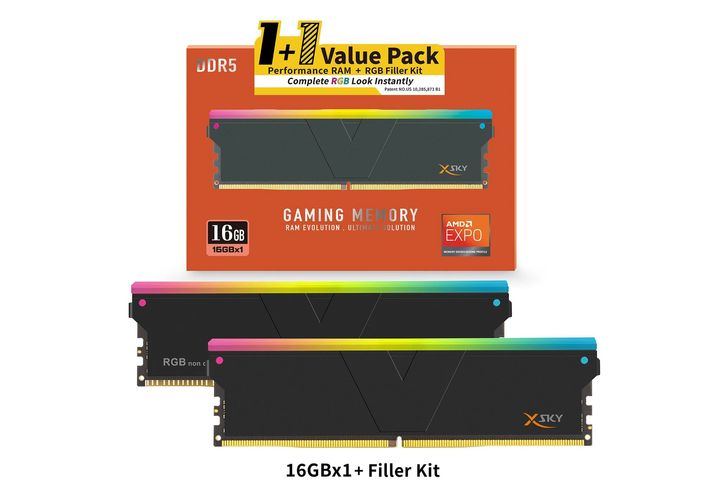

RAM kits are now sold with one fake RAM stick alongside a real one
Unscrupulous sellers are bundling fake RAM with real RAM to create an illusion of higher performance for AMD users, exploiting the ongoing memory shortage. This deceptive practice aims to provide desperate consumers with a temporary psychological relief as the supply crisis worsens.
Mouser: An open source alternative to Logi-Plus mouse software
I discovered this project because all-of-a-sudden Logi Options Plus software updater started taking 40-60% of my Intel Macbook Pro until I killed the process (of course it restarts). In my searches I ended up at a reddit discussion where I found other people with same issues.
I'm a minor contributor to this project but it aims to reduce/eliminate the need to use Logitech proprietary software and telemetry. We could use help if other people are interested.
Please check out the github link for more detailed motivations (eliminating telemetry) as a part of this project. Here is link: https://github.com/TomBadash/MouseControl
Hammerspoon
Michael Faraday: Scientist and Nonconformist (1996)
The article discusses the life and work of Michael Faraday, a pioneering scientist in the fields of electromagnetism and electrochemistry. It highlights Faraday's key contributions, including his discovery of electromagnetic induction and the principles of electrolysis, which laid the foundations for modern electrical engineering and electrochemistry.

Digg is gone again
Digg is a social news website where users can discover and share content from around the web. The platform allows users to vote on and comment on stories, with the most popular content being featured prominently.
Recursive Problems Benefit from Recursive Solutions
The article discusses the concept of recursion and its benefits in programming, highlighting its ability to simplify complex problems, improve code readability, and enable elegant solutions. It provides examples and insights into the advantages of using recursive functions to tackle various computational tasks.

Can I run AI locally?
CanIRun.ai is a machine learning-powered platform that analyzes running form and provides personalized feedback to help runners improve their technique and prevent injuries. The platform uses computer vision and AI algorithms to analyze videos of runners and offer insights on their stride, cadence, and other biomechanical factors.
Nominal Types in WebAssembly
The article discusses the introduction of nominal types in WebAssembly, a low-level, efficient, and portable binary instruction format. It explains how nominal types can improve WebAssembly's type system, enabling better type safety and more expressive programming.

I found 39 Algolia admin keys exposed across open source documentation sites
This article discusses the importance of Algolia DocSearch admin keys in managing search functionality for a website. It highlights the security implications of these keys and provides guidance on how to properly handle and protect them.
A Survival Guide to a PhD (2016)
This article provides a candid account of Andrej Karpathy's journey through a PhD program in machine learning, discussing the ups and downs, the challenges he faced, and the lessons he learned along the way.

Secure Secrets Management for Cursor Cloud Agents
The article discusses how Infisical, a secrets management platform, helps Cursor Cloud improve the security of its cloud agents by securely storing and managing sensitive information, ensuring compliance and reducing the risk of data breaches.
You gotta think outside the hypercube
The article discusses the concept of the 'hypercube' in computer science and how thinking outside of this rigid, multidimensional structure can lead to more creative and efficient solutions to complex problems. It encourages readers to challenge traditional mindsets and explore unconventional approaches to problem-solving.
![The Forth Language [Byte Magazine Volume 05 Number 08]](https://cdn.hazumi.news/eyJidWNrZXQiOiJoYXp1bWktaW1hZ2VzIiwia2V5IjoiNDczNzU5MzUiLCJlZGl0cyI6eyJyZXNpemUiOnsid2lkdGgiOjcyMCwiZml0IjoiY292ZXIifX19)
The Forth Language [Byte Magazine Volume 05 Number 08]
The August 1980 issue of Byte magazine features a wide range of articles covering topics such as microcomputer hardware, software, and applications, providing insights into the early days of the personal computing revolution.
I beg you to follow Crocker's Rules, even if you will be rude to me
The article discusses the history and importance of the Crocker Land Expedition, a failed 1913-1917 expedition that aimed to explore and map uncharted land north of Greenland. It highlights the expedition's scientific contributions and the challenges faced by the team, including their inability to locate the supposed Crocker Land.
Atari 2600 BASIC Programming (2015)
The article discusses the development of the Atari 2600 console and its unique BASIC programming language, which allowed users to create their own games and applications on the system. It provides an overview of the capabilities and limitations of the Atari 2600 BASIC and how it differed from traditional BASIC programming.

Games with loot boxes to get minimum 16 age rating across Europe
The article discusses a study that found the COVID-19 pandemic has led to significant declines in life expectancy in many countries, with the United States and England experiencing some of the largest reductions. The study highlights the profound impact the pandemic has had on population health globally.